Managing Bursitis
What is Bursitis?
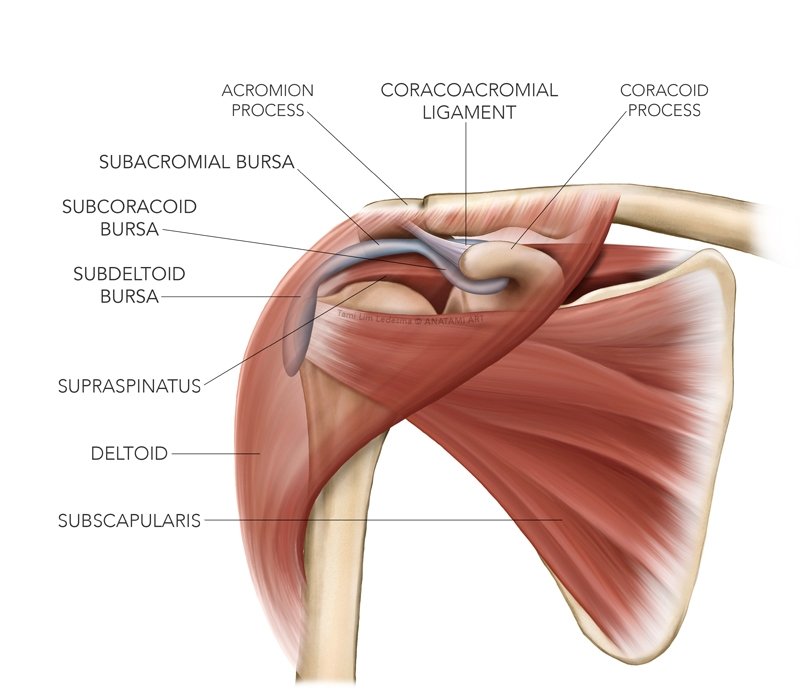
Bursitis is the inflammation or irritation of a bursa—a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction and cushions areas between bones, muscles, tendons, and skin. It commonly causes pain and discomfort in joints.
Common Types of Bursitis
Subacromial Bursitis (Shoulder Bursitis)
Pain and tenderness around the shoulder, particularly when raising the arm overhead.
Often worsened by repetitive movements, heavy lifting, or sleeping on the affected shoulder.
Greater Trochanteric Bursitis (Hip Bursitis)
Pain and tenderness on the outer side of the hip, often radiating down the thigh.
Pain may increase when lying on the affected side, walking, or climbing stairs
Common Causes
Repetitive motion or overuse from daily activities or sports
Injury or trauma
Sustained postures and biomechanics
Muscle weakness or reduced capacity
Age-related degenerative changes
Prognosis
Most cases of bursitis respond well to conservative treatment within weeks to months. Prompt management helps prevent chronic symptoms.
Assessing Tennis Elbow and Golfer’s Elbow
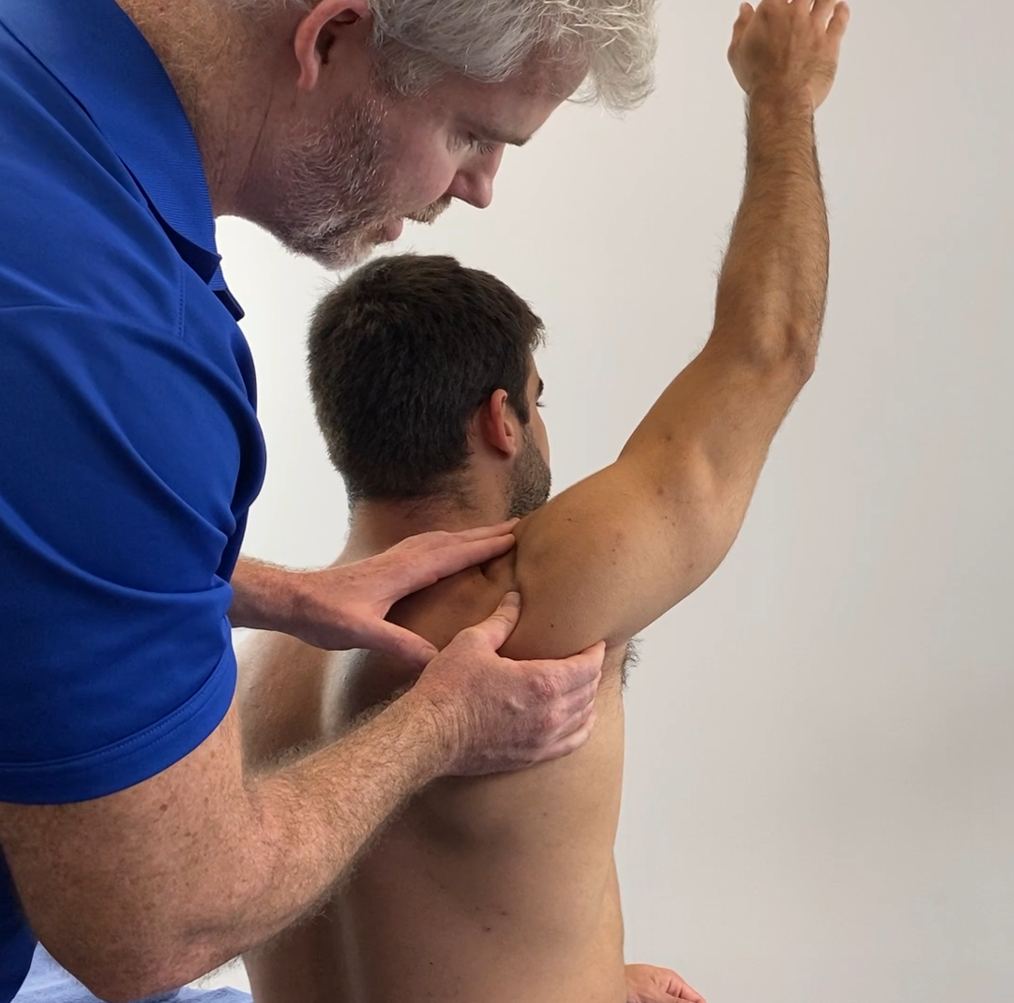
Clinical assessment typically involves:
Thorough patient history to understand activity patterns and symptom development
Physical examination focusing on tenderness, swelling, and joint mobility
Imaging (such as ultrasound or MRI), if required, to confirm diagnosis and rule out other conditions
Evidence-Based Management
Clinical guidelines recommend:
Activity Modification: Reducing activities that provoke symptoms.
Exercise and Rehabilitation: Strengthening, stretching, and improving posture to alleviate pressure on the bursae.
Manual Therapy: Gentle mobilisations and soft-tissue techniques to improve joint movement and decrease pain.
Pain Management: Short-term use of anti-inflammatory medications as per clinical recommendations.
Supportive Measures: Use of ice packs, cushioned pads, or assistive devices.
Injection Therapy: Corticosteroid injections in persistent cases, if clinically indicated.